Blockchain and ESG
Blockchain technology has emerged as a powerful tool that can revolutionize various industries, and one area where it holds significant potential is Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) practices. In this article, we will explore the intersection of blockchain and ESG, highlighting how this technology can contribute to advancing sustainability and transparency in business operations.

Blockchain Technology and ESG
Blockchain, often associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, is a decentralized and immutable ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. Its core features of transparency, security, and decentralization make it an ideal fit for addressing ESG challenges. By leveraging blockchain, organizations can enhance the traceability of their supply chains, increase accountability, and promote ethical practices.

Enhancing Supply Chain Traceability
Blockchain can play a pivotal role in improving supply chain transparency, a crucial aspect of ESG. By creating a tamper-proof record of every transaction and movement of goods, blockchain enables businesses to trace the origins of raw materials, monitor the environmental impact of production processes, and identify potential risks such as child labor or deforestation. This increased transparency not only helps companies adhere to sustainability goals but also allows consumers to make informed choices based on reliable information.
Empowering Decentralized Energy Systems
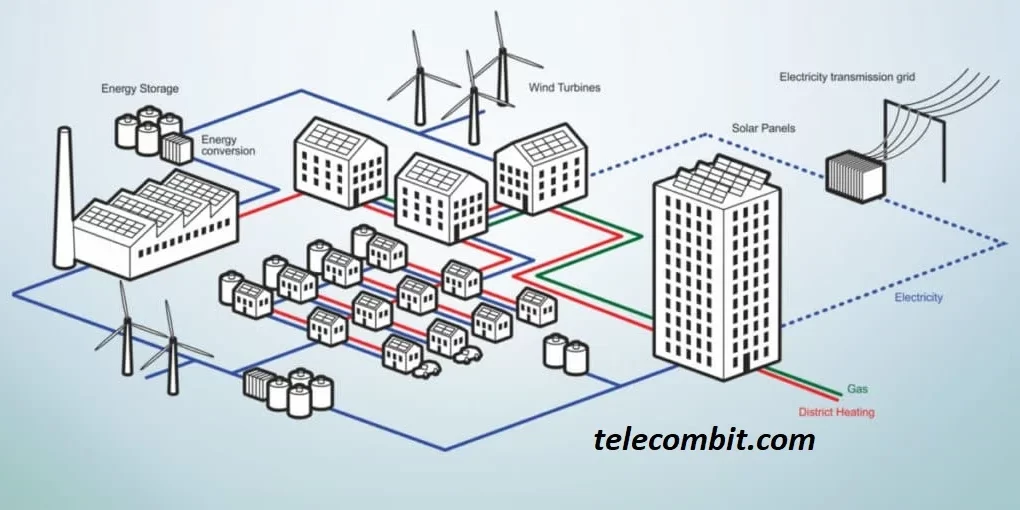
The energy sector is a major contributor to global carbon emissions. Blockchain technology can facilitate the development of decentralized energy systems, enabling peer-to-peer energy trading and efficient energy management. Through smart contracts and blockchain-enabled platforms, individuals and businesses can generate, store, and trade renewable energy directly, reducing reliance on centralized fossil fuel-based grids. This democratization of energy promotes sustainability and empowers communities to actively participate in the transition to clean energy sources.
Enabling Impactful Philanthropy and Social Finance
Blockchain can revolutionize philanthropy and social finance by providing transparency and accountability in charitable donations. With blockchain-based platforms, donors can track the flow of funds and ensure they reach the intended beneficiaries, eliminating the opacity and potential for corruption that often plague traditional donation systems. Additionally, blockchain-based cryptocurrencies can facilitate secure and instant cross-border transactions, making it easier to support social initiatives globally.

Improving Corporate Governance and Shareholder Engagement
Corporate governance is a vital component of ESG. Blockchain technology can enhance corporate governance by ensuring transparent and immutable shareholder voting systems. By recording votes on the blockchain, shareholders can participate in corporate decision-making, hold management accountable, and reduce the risk of fraudulent activities. This technology fosters trust among stakeholders and strengthens the alignment between a company’s actions and its stated ESG commitments.

Blockchain for Sustainable Supply Chain Certification
Blockchain can be utilized to certify and validate sustainability claims in supply chains. By storing certifications, audits, and sustainability data on a blockchain, stakeholders can easily verify the authenticity and accuracy of claims. This helps prevent greenwashing and provides a transparent mechanism for consumers to verify the sustainability credentials of products. Blockchain’s decentralized nature ensures that the data cannot be tampered with, enhancing trust and credibility in sustainable supply chain practices.
Facilitating Carbon Credit Trading
As the world focuses on reducing carbon emissions, blockchain can streamline and enhance carbon credit trading. By using blockchain as a distributed ledger for carbon credits, it becomes easier to track and verify the transfer of these credits between parties. Smart contracts can automate the process, ensuring that credits are accurately accounted for and reducing the complexity and cost associated with traditional carbon credit trading systems. This increased efficiency and transparency can incentivize companies to adopt cleaner technologies and practices.

Conclusion
Blockchain technology offers immense potential for driving sustainability and transparency in the realm of ESG. By leveraging its inherent features of decentralization, transparency, and immutability, businesses can enhance supply chain traceability, enable decentralized energy systems, promote impactful philanthropy, improve corporate governance, facilitate sustainable supply chain certification, and streamline carbon credit trading. Embracing blockchain can propel organizations towards their ESG goals, foster trust among stakeholders, and contribute to a more sustainable and responsible future.




